
Thailand News Info. The only country in south-east Asia to have eluded colonial rule, has a society and political system that has evolved under the sheltered umbrella of Buddhist beliefs and values, the beloved monarchy and more recently, the military.
Geography
Thailand, situated in the centre of the Indo-Chinese Peninsula, is bordered in the north, north-west and west by Myanmar, in the north, north-east and east by Laos, in the south-east by Cambodia and in the south by Malaysia. The coastline is on the Gulf of Thailand in the south and the Andaman Sea in the south-west. Thailand shares maritime boundaries with Cambodia and Vietnam in the Gulf of Thailand to the south-east, and with Indonesia and India on the Andaman Sea to the south-west.
Thailand covers a total area of 513,120 square kilometres, 510,890 of land and 2,230 of water and has a total coastline of 3,219 kilometres.
Thailand News Info
Topography
Thailand is divided into 6 geographical regions; North, North-East, East, West, Central and South. The Kingdom is divided into 76 provinces.

Thailand News Info
Capital City – Bangkok
The Kingdom’s Capital City was relocated to Thonburi when Ayutthaya fell to the Burmese armies in 1767.
King Rama I, the founder of the Chakri Dynasty, moved the Capital City to the other side of the Chao Phraya River, Bangkok in 1782, a more protected location as any potential Burmese threat to Thailand would come from the west. Bangkok became the new home of the Royal Family, and has remained so for over 220 years.
Bangkok as it is known Internationally, has the title of being one of the worlds longest words, “Krungthepmahanakhon Amonratanakosin Mahintharayutthaya Mahadilok Phopnopparat Ratchathaniburirom Udomratchaniwet Mahasathan Amonphiman Awatansathit Sakkathuttiya Witsanukamprasit”. For obvious reasons, this has been shortened to “Krung Thep” and it is still used by many Thai people.
Bangkok, “The City of Angels”, is populated by over 6 million people and is home to all the government ministries, the police and military headquarters and the Supreme Patriarch of the Buddhist faith. Thailand’s most prestigious universities and schools, cutting edge medical facilities, newspaper publishers, international companies and television stations also call Bangkok home.
Bangkok is a unique cultural phenomenon, laden with cultural and historical sites, temples, bustling night and street markets, ubiquitous street vendors and original architecture somehow interwoven with modern shopping Malls, international brands, world-class shopping and vibrant night-life. The city also has claims on having the best and most varied food on earth.
Bangkok is, without doubt, the shopping and culinary capital of Asia.
Transportation
Air
Thailand has 38 domestic and 10 international airports; Suvarnabhumi, Don Muang, Koh Samui, Phuket, Hat Yai, Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, Krabi, Udon Thani, and U-Tapao
Suvarnabhumi International Airport
AIRPORTS in THAILAND

Thailand News Info
Bangkok Airways owned, Koh Samui Airport, below.

Thailand News Info
Rail/Road
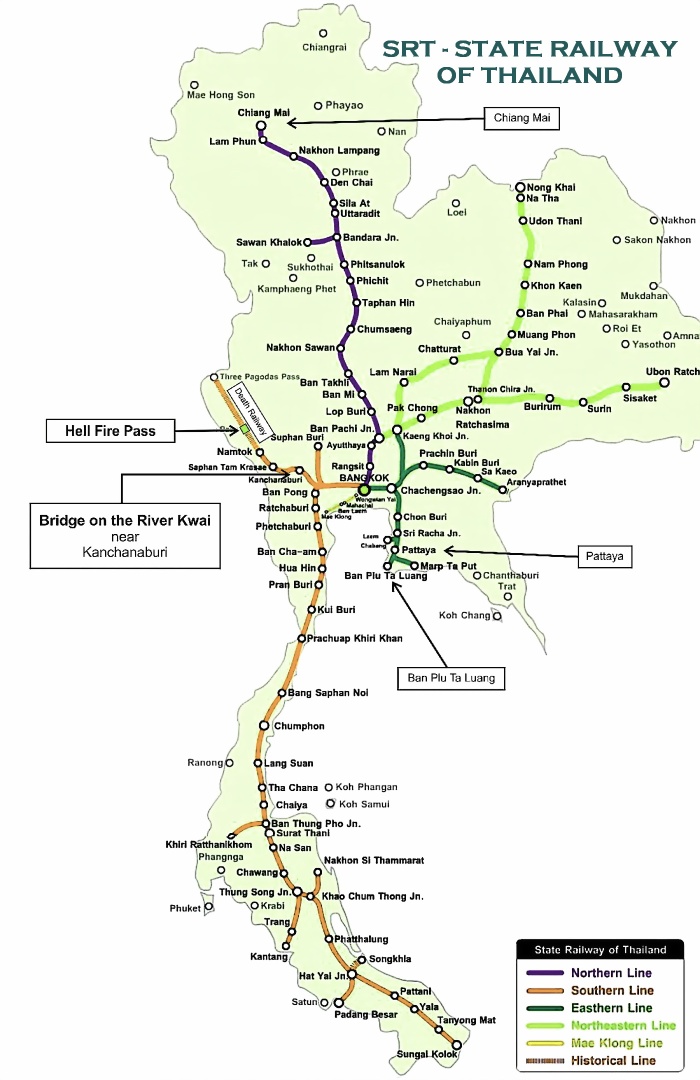
The northern and southern railways were merged and became the Royal State Railways of Siam/Thailand on June 5,1917. The various gauge tracks were all standardised to 1 metre gauge by 1930 to be compatible with the bordering countries. There is now 4,043 kilometres of railway, 1,928 minor and 1,662 major railway crossings, 117 road underpasses and 144 overpasses throughout Thailand.

Thailand News Info
The State Railway connects Bangkok with northern, north-east and central Thailand while a southern route allows direct rail travel from Bangkok to Malaysia and Singapore.
After long delays in construction and several test runs, Suvarnabhumi Airport’s Link commenced commercial services Monday, 23 rd August, 2010. The Express Service is a 15-minute non-stop journey between the City Terminal and the airport.
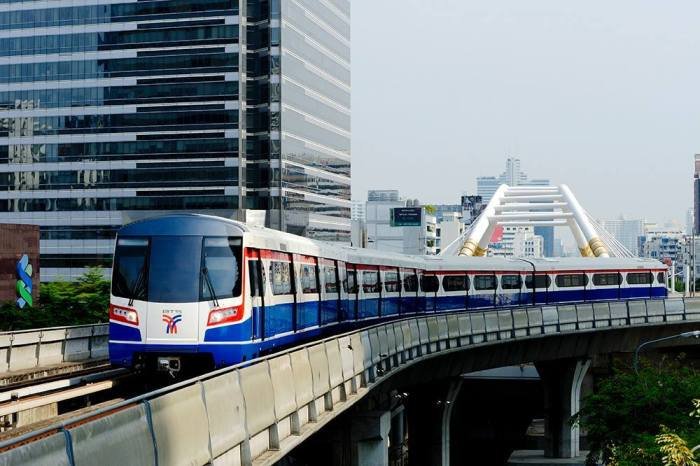
Inside central Bangkok, it is extremely easy. The Bangkok MRT and BTS Sky-train (above) or cheap metered taxis, that are very inexpensive by overseas standards, will satisfy the needs of most commuters. With a little bit more spirit of adventure, you can beat any traffic jams on a motorcycle taxi, or get out and around the suburbs in the abundance of minivans which zip around and big modern government buses.
In Thailand the road law is to drive on the left side of the road. There are over 176,000 kilometres of national, rural and local highways, linking small towns, provincial capitals and major cities.
All in one transit guide

Thailand News Info
Population
Thailand’s population is 69.9 million with a population density of approximately 117 people per square kilometre.
The population in Bangkok, the capital city of Thailand, is approximately 8 million people with a population density of approximately 5,111 people per square kilometre.
Ethnic Groups
Thai 95.9%, Burmese 2%, other 1.3%, unspecified 0.9%
Though the great majority of Thailand is ethnically Thai and Buddhist, the country has a substantial number of minority groups who have historically lived together in harmony.
The Chinese are perhaps the most numerous, particularly in urban areas, though they have become so thoroughly assimilated it would be difficult to isolate them as a distinct group. Similarly, while there are Lao and Khmer groups in the North-east and East, nearly all regard themselves as Thai, culturally as well as by nationality.
More clearly defined as an ethnic group are the Muslims, who are mainly concentrated in the southern provinces, and assorted hill tribes who live in the far North; there are also sizable communities of Hindus and Sikhs in large cities like Bangkok.
Culture – Thai Wai
The wai is the common form of greeting and adheres to strict rules of protocol. However in recent times, especially in tourist areas, Thai people have become very forgiving if the Wai is not performed correctly. They appreciate the fact that you have made an attempt to be polite and are respectful of their culture.
Thailand News Info
- Raising both hands, palms joined with the fingers pointing upwards as if in prayer, lightly touching the body somewhere between the chest and the forehead, is the standard form.
- The wai is both a sign of respect as well as a greeting. Respect and courtesy are demonstrated by the height at which the hands are held and how low the head comes down to meet the thumbs of both hands.
- The wai may be made while sitting, walking, or standing.
- The person who is junior in age or status is the first one to offer the wai.
- The senior person returns the wai, generally with their hands raised to somewhere around their chest.
- If a junior person is standing and wants to wai a senior person who is seated, the junior person will stoop or bow their head while making the wai.
- If there is a great social distance between two people, the wai will not be returned.
Culture – Hierarchical Society
Thais respect hierarchical relationships.
- Social relationships are defined as one person being superior to the other.
- Parents are superior to their children, teachers to their students, and bosses to their subordinates.
- When Thais meet a stranger, they will immediately try to place you within a hierarchy so they know how you should be treated.
- This is often done by asking what might be seen as very personal questions in other cultures.
- Status can be determined by clothing and general appearance, age, job, education, family name, and social connections.
Culture – Thai Family Values
The family is the cornerstone of Thai society.
- Family life is often more closely knit than in western cultures.
- The Thai family is a form of hierarchy with the parents at the top.
- Children are taught to honour their parents.
Culture – Thai Demeanour
Thais place great emphasis and value on outward forms of courtesy such as politeness, respect, genial demeanour and self-control in order to maintain harmonious relations.
- Many of their rules of etiquette are by-products of the Buddhist religion.
- It is a non-confrontational society, in which public dispute or criticism is to be avoided at all costs.
- To be openly angry with someone might attract the wrath of the spirits, which in turn could cause violence and tragedy.
- Openly criticizing a person is a form of violence as it hurts the person and is viewed as a conscious attempt to offend the person being rebuked
- Loss of face is a disgrace to a Thai so they try to avoid confrontations and look for compromises in difficult situations.
- If two parties disagree, one will need to have an outlet to retreat without losing face.
Culture – Dining Etiquette
If you are invited to a Thai’s house:
- Arrive close to the appointed time, although being a few minutes late will not cause offence.
- Check to see if the host is wearing shoes. If not, remove yours before entering the house.
- Ask another guest to confirm the dress code.
- Step over the threshold rather than on it. This is an old custom that may be dying out with younger Thais, but erring on the side of conservatism is always a good idea.
Thailand News Info
Culture – Table manners
A fork and spoon are the usual eating utensils. However, noodles are often eaten with chopsticks.
- The spoon is held in the right hand and the fork in the left. The fork is used to guide food on to the spoon. Sticky rice, a northern Thai delicacy, is often eaten with the fingers of the right hand.
- Most meals are served as buffets or with serving platters in the centre of the table family- style.
- You may begin eating as soon as you are served.
- Leave a little food on your plate after you have eaten to show that you are full. Finishing everything indicates that you are still hungry.
- Never leave rice on your plate as it is considered wasteful. The words for food and rice are the same. Rice has an almost mystical significance in addition to its humdrum ‘daily bread’ function.
- Never take the last bite from the serving bowl.
- Wait to be asked before taking a second helping.
- Do not lick your fingers.
The forgiving, non-confrontational and respectful Thai culture influenced by decades of Buddhist beliefs have made Thailand and its people possibly the most amiable and courteous civilization in the world.
Thailand News Info
Weather – Seasons
Countrywide, the average annual high is 38° C (100.4° F) and the average annual low is 19° C (66.2° F). This is accompanied by a high level of humidity, often exceeding 70%.
From a meteorological point of view, the climate of Thailand may be divided into three seasons as follows:
Rainy or south-west monsoon season (mid-May to mid-October)
The south-west monsoon prevails over Thailand and abundant rain occurs over the country. The wettest period of the year is August to September. The exception is found in the Southern Thailand East Coast where abundant rain remains until the end of the year that is the beginning period of the north-east monsoon and November is the wettest month.
Winter or north-east monsoon season (mid-October to mid-February)
This is the mild period of the year with quite cold in December and January in upper Thailand but there is a great amount of rainfall in Southern Thailand East Coast, especially during October to November.
Summer or pre-monsoon season (mid-February to mid-May)
This is the transitional period from the north east to south-west monsoons. The weather becomes warmer, especially in upper Thailand. April is the hottest month.
Thailand News Info
Monthly Weather History and Forecast
Bangkok
Thailand News Info
Language
The Thai language is comprised of 44 consonants, 32 vowels and five tones in Thai pronunciation, along with a script that has Indian origins. The Thai language, belonging to the Tai family, is the main language in Thailand although there are several regional dialects as well. Other languages spoken in Thailand are Chinese, Lao, Malay and Mon-Khmer, while English use is becoming more prevalent in government and commerce. English is also being taught as a second language in secondary school and universities, which enables the English speaking visitor in Thailand to have little trouble conversing.
Religion
Buddhist 93.6%, Muslim 4.9%, Christian 1.2%, other 0.2%, none 0.1%.
Thailand is a stronghold of Buddhism, which dates back 2556 years to the time of Buddha, and Buddhists believe that life does not begin with birth and end with death, but that every person has several lives based upon the lessons of life not yet learned and acts committed (karma) in previous lives. The History of Buddhism started with the birth of Buddha Siddhartha Gautama on the Indian subcontinent, in Lumbini Nepal. It is one of the oldest religions (if you consider it to be a religion) practised today evolving as it spread from the north-east of the Indian subcontinent through Central, East and South-East Asia. At one time or another, it influenced most of the Asian continent.
Buddhism in Thailand is represented primarily by the presence of Buddhist monks, who serve as officiates on ceremonial occasions, as well as being responsible for preserving and conveying the teachings of the Buddha. Prior to the creation of state-run primary schools in Thailand, village temples served as the primary form of education for most Thai boys. During the latter half of the 20th century, most monks in Thailand began their careers by serving as dek wat (literally, children of the wat). Dek wat are traditionally no younger than eight, and do minor housework around the temple. Service in a temple as a dek wat was a necessary prerequisite for attaining any higher education, and was the only learning available to most Thai peasants.
Royal Thai Government
The democratically elected government has had many interruptions over the last century, since 1947 Thailand has been ruled by the army for more years than the elected government.
The government of Thailand is currently conducted within the framework of a constitutional democratic monarchy, whereby the Prime Minister is the head of government and a hereditary monarch, currently His Majesty King Bhumibol Adulyadej, is the Head of State.
The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislative branches.
The governance in Thailand is formed and operated on the basis of the constitution and according to it; the political system of Thailand is divided into three branches; executive, legislative and judicial.

Thailand News Info
The Executive Branch of the Government
The executive branch is headed the Prime Minister, who, since the amendment of the 1992 constitution, must be an MP. The cabinet is responsible for the administration of fourteen ministries, and the Office of the Prime Minister.
Each ministry is headed by a politically appointed minister, and in most cases, at least one deputy minister. The Prime Minister is assisted by Deputy Prime Ministers as well as a number of ministers holding the portfolio of “Minister to the Prime Minister’s Office.” The constitution of 1997 limits the number of cabinet members to 36.
The Office of the Prime Minister is a central body, which in itself ranks as a ministry, whose responsibility is largely concerned with formulating national policy. Some of its primary subdivisions are the Budget Bureau, the National Security Council, the Juridical Council, the National Economic and Social Development Board, the Board of Investment, the Civil Service Commission and several other organisations vital to the formulation of national policy.
The Legislative Branch of the Government
This is the law making section of the government which is also known as The National Assembly.
This branch of the Thai Government consists of the following two divisions;
The House of Representatives – This is the lower house of the legislative branch and consists of 500 members of the Parliament who are elected popularly. Four hundred are district MPs, directly elected in each constituency and each representing approximately 150,000 people. The remaining hundred are party-list MPs, who are elected indirectly by the percentage of vote the party receives
The Senate – This is the upper house of the legislative branch of the government and has 200 members. Under the 1997 promulgated Constitution, these senators were directly elected for the first time on 2 March 2000, although the Constitution requires all senatorial candidates to be an independent with no party affiliations.
This section of this branch is responsible for enactment of all the organic laws
The Judicial Branch of the Government
The third branch or arm of the government is the judicial branch which is responsible for making sure that all laws made by the legislative branch are properly enforced. This branch basically consists of all the courts of Thailand.
The Constitutional Court – This is the most important court in Thailand and holds the power to review the application of any law that was involved in any previous case. The powers that this court holds are wide and very broad.
The Supreme Court – The Supreme Court and constitutional court are different bodies in Thailand.
The Appeal Courts – This is the second most powerful type of court category in Thailand and consists of those courts which are authorized to consider the appeal from trial courts.
The Trial Courts – These are the base levels courts in Thailand which consist of many courts including the; District courts, Provincial courts, Central courts-central criminal courts and central civil courts, Labor courts, Military courts, Juvenile courts, Family courts
and the International trade and intellectual property courts.
Kingdom of Thailand, Coat of Arms 2007

Thailand News Info. Armed Forces of Thailand
The King is the Commander-in-Chief of the Royal Thai Armed Forces and the cabinet is
the instrument through which national security policies are formulated. The Defence Ministry coordinates the administration of the Armed Forces, which are divided into three branches: the Royal Thai Army (RTA), the Royal Thai Navy (RTN) and the Royal Thai Air Force (RTAF).
Thai soldiers are composed of professional career soldiers and conscripts. Every Thai male
between the age twenty-one and twenty-five is subject to two years of military service.
Thailand’s fighting forces are governed by the Supreme Command Headquarters, which
is staffed by leaders of the Army, Navy and Air Force.
Organised into divisions and combat regiments, the Royal Thai Army is divided into four army regions, covering Bangkok and the Central Plains, the North-east, the North and the South. Thailand’s naval fleet, based at Sattahip, South-east of Bangkok, is small but well-trained. It includes the Marine Corps, modelled on the American pattern, which is skilled in both amphibious and jungle operations.
The Royal Thai Air Force, on the other hand, has its main base at Don Muang airport in Bangkok and large air fields and facilities in the North and North-east.
National Flag
Thailand’s national flag, ceremoniously raised each morning in every town and village, is composed of five horizontal bands of red, white, and blue.
- Red represents the nation
- White evokes religion
- Blue symbolizes the monarchy

Thailand News Info
This three coloured flag, consisting of five horizontal bands of red, white, blue (double width), white and red, is called in Thai, the “trirong”. The flag was first introduced by King Vajiravudh (Rama VI) in 1917, and succeeded seven previous designs that are shown below.

Thailand News Info
Economy
Thailand is an export oriented economy with exports accounting for around 65 % of the GDP.
The country mainly exports manufactured goods (86 % of total shipments) with electronics (14 %), vehicles (13 %), machinery and equipment (7.5 %) and foodstuffs (7.5 %) being the most important.
Agricultural goods, mainly rice and rubber, account for 8 % of total shipments.
Thailand’s major export partners are China (12 %), Japan (10 %), the United States (10 %) and the European Union (9.5 %). Others include: Malaysia, Australia and Singapore.
Year
The Thai Buddhist year is calculated by adding 543 to the current Gregorian year.
The Buddhist year for 2016 is 2559.
Time
Thailand’s standard time is UTC+7; 7 hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time.
Currency
Thailand’s currency is the baht, which is divided into 100 satang.
Coins are valued at 25 and 50 satang and 1, 2, 5, and 10 baht.
Bank notes are valued at 20, 50, 100, 500 and 1,000 baht.
Please note, the banknotes in the photo below are not to scale.


Thailand News Info
Business Hours
In Thailand, businesses are open Monday to Friday from 8.30 am to 5.00 pm, with an hour for lunch between 12.00 – 01.00 pm. Shopping centres and supermarkets are generally open from 10.00 am – 09.00 pm daily.
Banking Hours
Monday to Friday, from 9.30 am. to 3.30 pm.
Electricity
Voltage in Thailand : 220 Volt
Frequency in Thailand : 50 Hz per second
I have seen 4 different types of wall socket in Thailand. So you will need to bring or buy an adapter for charging of phones and laptops. These are the 4 common plugs in Thailand.
You can use your electric appliances in Thailand, if the standard voltage in your country is between 220V – 240V , as in the UK, Europe, Australia and most of Asia and Africa.
The Television system in Thailand is PAL.
Education
6 years – Primary school
3 years – Secondary school
3 years – High school
4 years – College/University
Telephone
Country code for Thailand is 66. Bangkok area code is 02.
Telephone charge for home phone is normally 3 baht for one time use in the same area code, regardless of the length of the call. There are two types of public phone available; coin type and telephone card type.
Holidays
The annual celebrations and national holidays are mainly related to the Monarchy and Buddhism. Official working days are Monday to Friday.
Thailand News Info


Thailand News Info
[wp-review id=”28091″]











Visitor Rating: 5 Stars
Visitor Rating: 5 Stars
Visitor Rating: 5 Stars